| January 2005 | ||||||
| Sun | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||
| Dec Feb | ||||||
Report from the ESA on the latest Huygens findings on Titan....
Seeing, touching and smelling the extraordinarily Earth-like world of Titan
|
21 January 2005
ESA PR 05-2005. On 14 January ESA's Huygens probe made an historic first ever descent to the surface of Titan, 1.2 billion kilometres from Earth and the largest of Saturn's moons. Huygens travelled to Titan as part of the joint ESA/NASA/ASI Cassini-Huygens mission. Starting at about 150 kilometres altitude, six multi-function instruments on board Huygens recorded data during the descent and on the surface. The first scientific assessments of Huygens' data were presented during a press conference at ESA head office in Paris on 21 January.
"We now have the key to understanding what shapes Titan's landscape," said Dr Martin Tomasko, Principal Investigator for the Descent Imager-Spectral Radiometer (DISR), adding: "Geological evidence for precipitation, erosion, mechanical abrasion and other fluvial activity says that the physical processes shaping Titan are much the same as those shaping Earth."
| |||
|
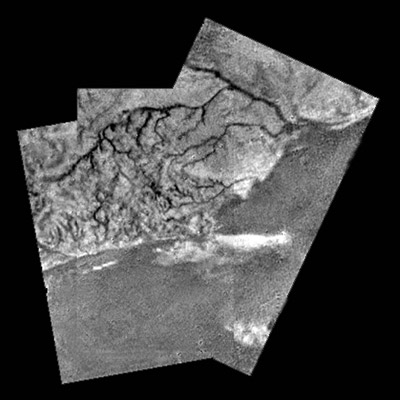
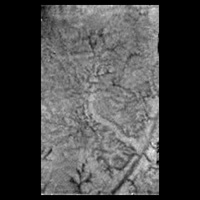
"Islands in the stream"... possible 'islands' on a dark plain |
Data provided in part by the Gas Chromatograph and Mass Spectrometer (GCMS) and Surface Science Package (SSP) support Dr Tomasko's conclusions. Huygens' data provide strong evidence for liquids flowing on Titan. However, the fluid involved is methane, a simple organic compound that can exist as a liquid or gas at Titan's sub-170°C temperatures, rather than water as on Earth.
Titan's rivers and lakes appear dry at the moment, but rain may have occurred not long ago.
Deceleration and penetration data provided by the SSP indicate that the material beneath the surface's crust has the consistency of loose sand, possibly the result of methane rain falling on the surface over eons, or the wicking of liquids from below towards the surface.
|
|||
|
Two new Titan features - water ice and methane springs |
In addition, DISR surface images show small rounded pebbles in a dry riverbed. Spectra measurements (colour) are consistent with a composition of dirty water ice rather than silicate rocks. However, these are rock-like solid at Titan's temperatures.
Titan's soil appears to consist at least in part of precipitated deposits of the organic haze that shrouds the planet. This dark material settles out of the atmosphere. When washed off high elevations by methane rain, it concentrates at the bottom of the drainage channels and riverbeds contributing to the dark areas seen in DISR images.
New, stunning evidence based on finding atmospheric argon 40 indicates that Titan has experienced volcanic activity generating not lava, as on Earth, but water ice and ammonia.
| |||
|
Titan landing site seen from Cassini |
Titan is an extraordinary world having Earth-like geophysical processes operating on exotic materials in very alien conditions.
|
|||
|
Panel of scientists presenting Huygens results |
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperation between NASA, ESA and ASI, the Italian space agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, is managing the mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington DC. JPL designed, developed and assembled the Cassini orbiter while ESA operated the Huygens atmospheric probe.
For further information, please contact :
ESA Media Relations Division
Tel: +33(0)1.53.69.7155
Fax: +33(0)1.53.69.7690
1:21:30 PM